Every camera is equipped with an intelligence which is called metering. In some camera, it is controlled by the user, and in some it is fully automated. Metering in camera determine correct exposure. In DSLRs or in advanced compact cameras there are various modes which helps the photographer to control the exposure. Before getting into various modes, lets understand the basics of light metering.
Light meters can be divided into following two categories.
Incident Light Meter measures the brightness of the subject on the basis of the light falling on the subject. It gives correct exposure because the incident light will be the same no matter reflectance of the subject. The measurement is taken place by placing a light meter in front of the subject.
Reflective Light Meter measures the brightness of the subject based on the reflected light by the subject. Because it measures the reflected light, it is more practical and convenience to use in most of the situations.
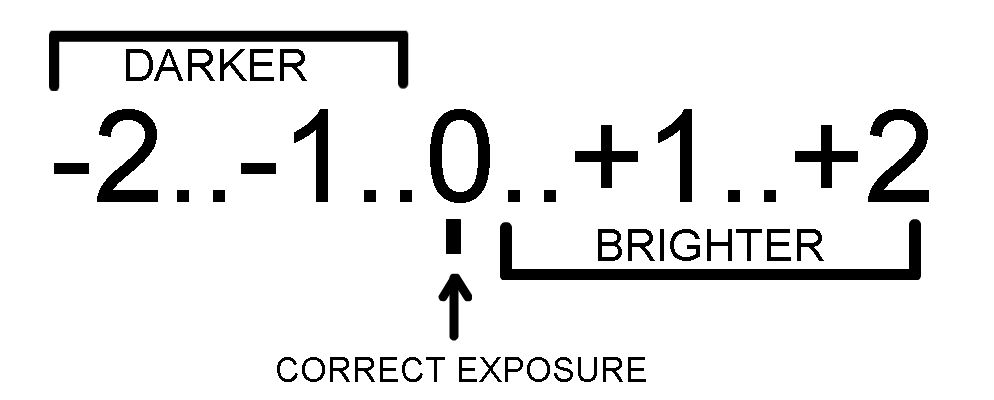
A camera equipped with a Reflective Light Meter. The camera meter is calibrated to calculate the proper exposure for a subject by of an average brightness. In order to get proper exposure most of the camera meter evaluates a monochrome version of the subject and sues mid tone middle gray as the baseline. Dark gray approaching black are treated opposite to the light gray approaching white. Most of the camera shows a graphical representation of the light meter. It shows the scale in the viewfinder, LCD screen on top and on the back side of the camera.
Modes
On the basis of the information provided by the camera you can take a decision whether to alter the exposure or go with the suggested exposure.
Now we understand the camera uses reflected light, lets now understand from which part of the frame the camera reads the light. The answer lies in the metering mode.
Over the years, the camera metering modes has become more precise and sophisticated. However basic modes are still divided into following three categories.
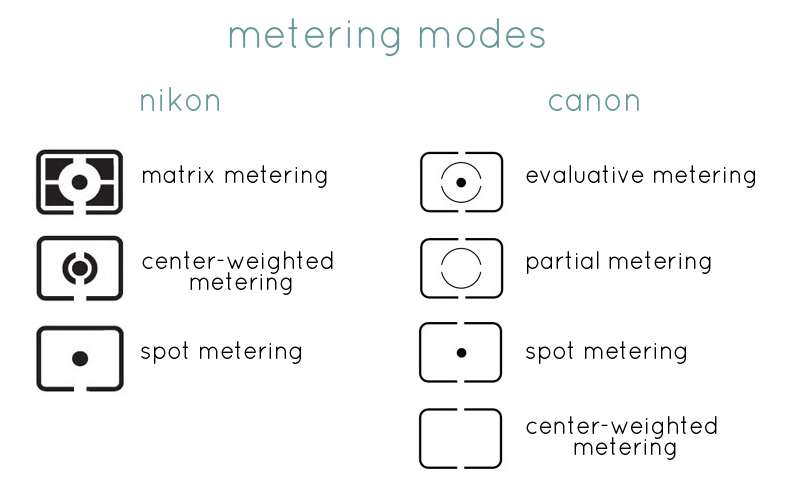
Matrix / Evaluative metering mode: In this mode, the camera takes reflective light information from the entire scene and average out the information. This mode is linked to the active autofocus point. The camera meter measures the brightness of the area around the autofocus point and compares it with the rest of the scene to get proper exposure. It also takes into account the subject brightness, contrast, color information into account to ascertain the proper exposure.
This mode is most widely used because in almost all the situations it gives pretty good result.
Centre Weighted metering mode: In this mode, the camera averages out the light information from the entire scene but gives weightage to the information gathered from the center area of the scene. Unlike the Matrix / Evaluated metering mode the camera does not consider the active focus point.
This mode is used for the images where the center area of the frame is most important, like close up portrait.
Spot Metering mode: In this mode, the camera evaluates the light around your single focus point and ignores the rest. This allows you to meter reflective light from a very small portion of the scene. The camera allows you to move the spot to the different area of the frame by shifting the focus point manually.
This mode is used for the images where a small portion of the scene has to be exposed properly particularly on a high dynamic range image, like eyes of a subject or wildlife photograph.
Partial Metering mode: Partial metering mode works similar to spot metering mode. Only difference is this mode takes exposure from a slightly bigger area around the focus point.
This mode can also be used in the similar situations as Spot metering.
Today’s camera metering system is very precise however tricky lighting situation sometime fools the reflective metering system. The in-camera reflective metering system works perfectly when the entire scene works around the mid tone range. Scenes like snowscape, sunset, sunrise, high key or low key images are difficult to shoot with automatic metering system. Therefore, be prepare to experiment with your own experience.